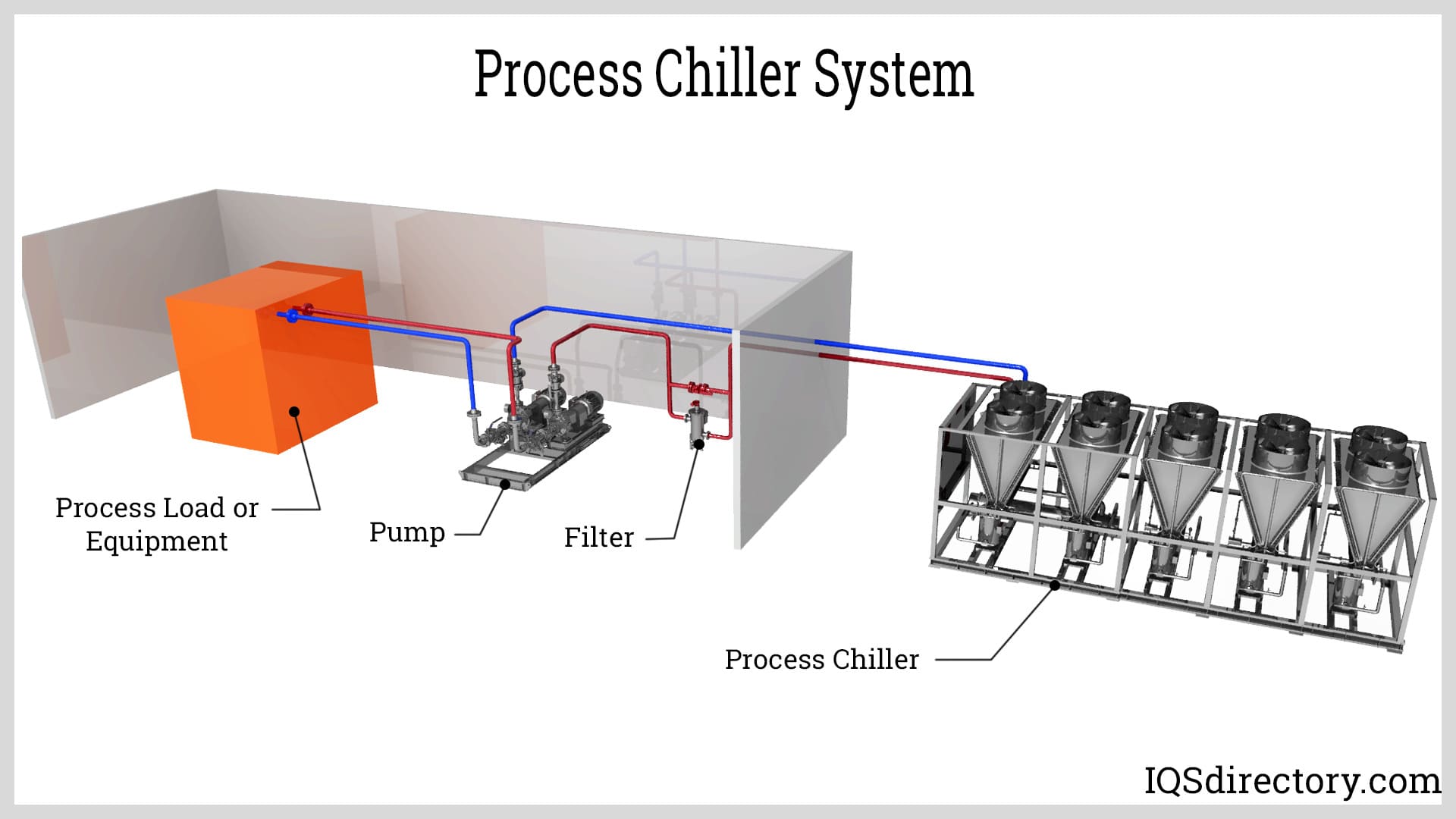
Industrial chillers are designed to remove heat from machinery and workspaces and process fluids. They are an essential part of temperature regulation for industrial processes such as injection molding, metal plating, and food processing. The four basic components of an industrial chiller are an evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve, which work together using a refrigerant to maintain consistently low temperatures by removing heat. Read More…
Our customers know they can trust us for the ultimate in quality, affordability, and flexibility. If you want a fully customized solution for your chillers, we can help! We work hard to create the best solution for each of our customers, because we know that if you are not happy, we are not happy! You can learn more about our services by visiting our website or giving us a call today!

Dimplex Thermal Solutions, based in Kalamazoo, Mich., and home of Koolant Koolers, has been manufacturing water, air, and glycol chillers since 1952. Since that time Dimplex has expanded it’s product offering to include industrial cooling for: Machine Tooling, Food Processing and Packaging, Medical Diagnostic Imaging, Laser Cutting, Manufacturing Processes and more. Dimplex is known for their...
At Tark Thermal Solutions, we position ourselves as a dedicated partner in advanced cooling technology, delivering liquid chillers that support precise temperature control across demanding applications. We design and build our systems with a focus on reliability, thermal stability, and energy efficiency, tailoring each unit so it performs consistently in environments where process accuracy...
We are ChillX Chillers, and we take pride in engineering and manufacturing reliable, high-performance chillers designed to meet the cooling needs of businesses across a wide range of industries. Our focus has always been on combining innovation, energy efficiency, and durability, which is why our chillers are trusted for everything from process cooling and manufacturing applications to...
More Industrial Chiller Manufacturers

The types of chillers are water cooled and air cooled, divided into vapor absorption chillers and vapor compression chillers, each of which uses a different technique for removing the collected heat from the chiller system. In the case of an air cooled chiller, fans remove heat from the chiller by circulating air. With water cooled chillers, heat from the process is removed by water. Absorption chillers use a concentrated absorbent agent such as lithium bromide or ammonia water to absorb the coolant while the heat is removed by cooling water.
Types of Industrial Chillers
Although the majority of chillers are air or water cooled, some of the distinguishing features that separate the different types of chillers is the type of compressor they use. Vapor compression chillers use an electrically driven mechanical compressor to force refrigerant through the system. The more popular types of chillers are vapor absorption chillers, divided between air cooled and water cooled.
Vapor Compression Chillers
Most of the components of a vapor compression chiller are the same as vapor absorption chillers, which are an evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve. However, what differentiates vapor compression chillers from vapor absorption ones is the absence of a compressor. Instead, vapor compression chillers have an electrically driven mechanical compressor that forces the refrigerant through the system.
The principle behind the operation of a vapor compression chiller is the same as all chillers, which is to remove heat and replace it with cool air. They use a refrigerant that absorbs heat from a space and brings it back to the evaporator that removes the heat, using fans for an air cooled chiller or water for a water cooled one. Aside from the driving mechanism of a vapor compression chiller, the other basic functions are the same.

Vapor Absorption Chiller
Vapor absorption chillers work on the principle of separating and recombining fluids, such as refrigerant and absorbent, to create cooling. The process of an absorption chiller includes ammonia water cycling or lithium bromide cycling. With ammonia water vapor absorption chillers, water serves as the absorbent while an ammonia-water solution acts as the refrigerant. In a lithium bromide system, lithium bromide is the absorbent, while water is the refrigerant.

Air Cooled Systems vs. Water Cooled Systems
Once the chiller system collects the heat, it has to be removed and released into the atmosphere. For all industrial chiller systems, two methods are used to achieve this: air cooling and water cooling. These two methods are a major factor in determining certain aspects of the overall chiller system.
-
Air Cooled
Air cooled systems use the surrounding air of the chiller to eject the air out of the system and into the atmosphere. They consist of propeller-driven fans to pull air over the condenser's coils. As the air moves over the coils, heat is transferred to the air and released into the atmosphere. Major factors in the use of air cooled chillers are their size and ease of installation. Since they use the ambient air for the heat transfer process, they can be installed outside of a building or on its roof.
-
Water Cooled
Water cooled chillers have water cooled condensers connected to a cooling tower. The essential element for water cooled chillers is circulating water that comes from the cooling tower and cools the gaseous form of the refrigerant. Once the refrigerant gas is cooled, it undergoes a phase change back to a liquid and is recirculated through the system.
Unlike air cooled chillers, water cooled chillers are normally located inside a building, which protects them from the effects of the elements. They are more efficient and produce less noise than air cooled chillers. However, water cooled systems are expensive and take up more room due to the use of cooling towers.
Types of Compressors
The compressor of a chiller removes the heat from the refrigerant by taking low-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant in a gaseous form and compressing it into a high-pressure and high-temperature form. Once the refrigerant has been compressed, it moves on to the condenser coils, where heat is removed using water or air.
Centrifugal Compressor
A centrifugal compressor has impellers that rapidly rotate the refrigerant and force it to the compressor's walls. As the rate of the revolutions increases, the pressure and temperature in the refrigerant rise; then, it is released to the condenser. Centrifugal compressors are used with high capacity, large systems of up to 6000 tons.
Reciprocating Compressor
A reciprocating compressor has a piston, cylinder, and crankshaft. The gas enters the cylinder through the intake by the reverse movement of the piston that sucks it in. Once the chamber of the cylinder is full, the reciprocating motion of the piston compresses the gas and discharges it into the condenser.
Scroll Compressor
Scroll compressors have two spiral plates with one stationary and one rotating. As the rotating plate spins, it compresses the refrigerant. During the motion of the moving plate, small pockets of refrigerant are pushed between the scrolls, reducing the volume of the refrigerant.

Screw Compressors
Screw compressors have two intermeshed helical rotors with male lobes and female gullies that compress the refrigerant and increase its pressure. They are the quietest type of compressor and have fewer moving parts. The suction, compression, and discharge happen in a single linear motion.
Choosing the Right Industrial Chiller Company
For the most constructive outcome when purchasing an industrial chiller from an industrial chiller supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of suppliers. Each industrial chiller company includes a business profile page highlighting their areas of expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with them for more information or request a quote. Review each industrial chiller business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RDQ form to contact multiple industrial chiller businesses with the same form.





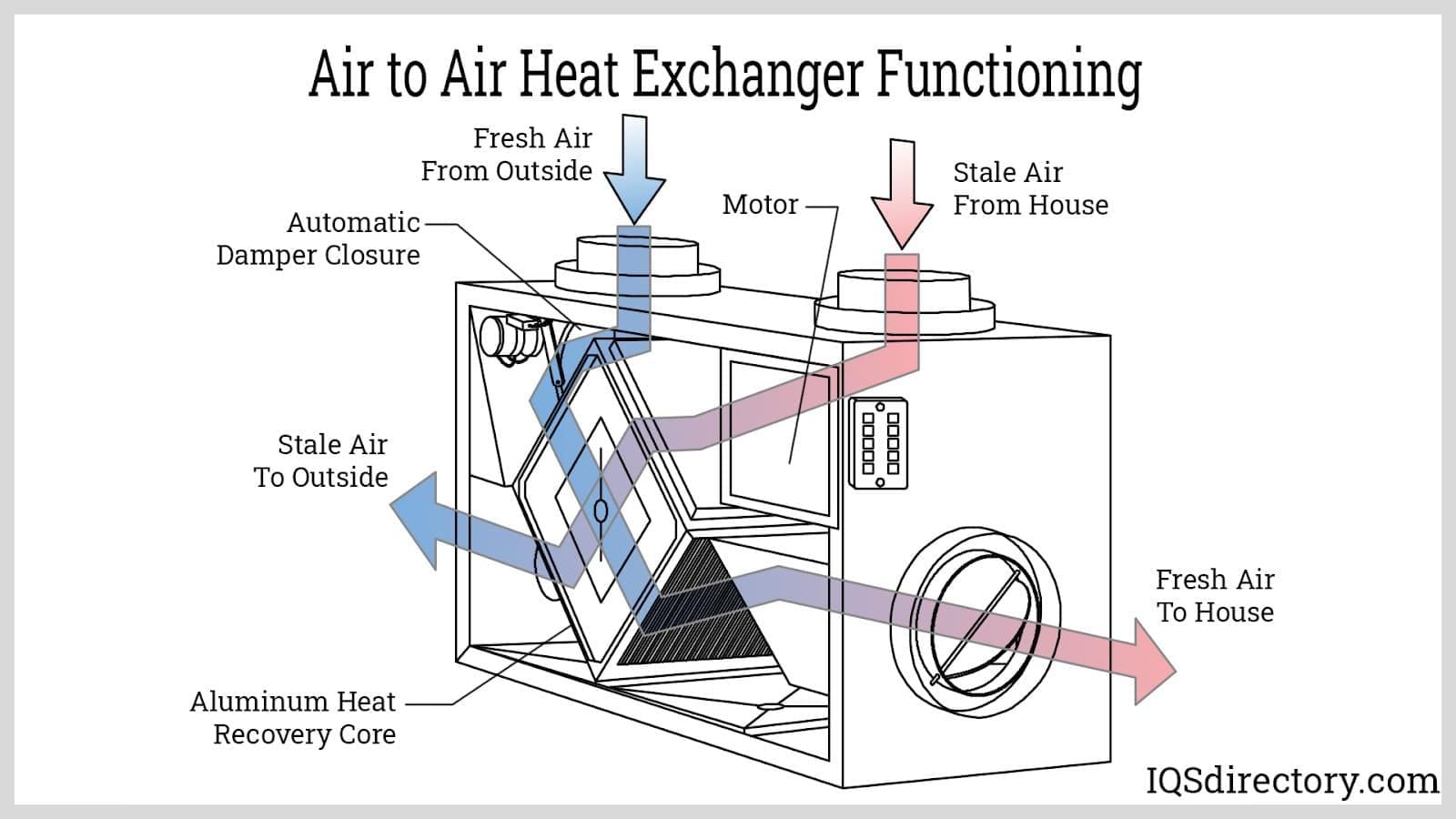

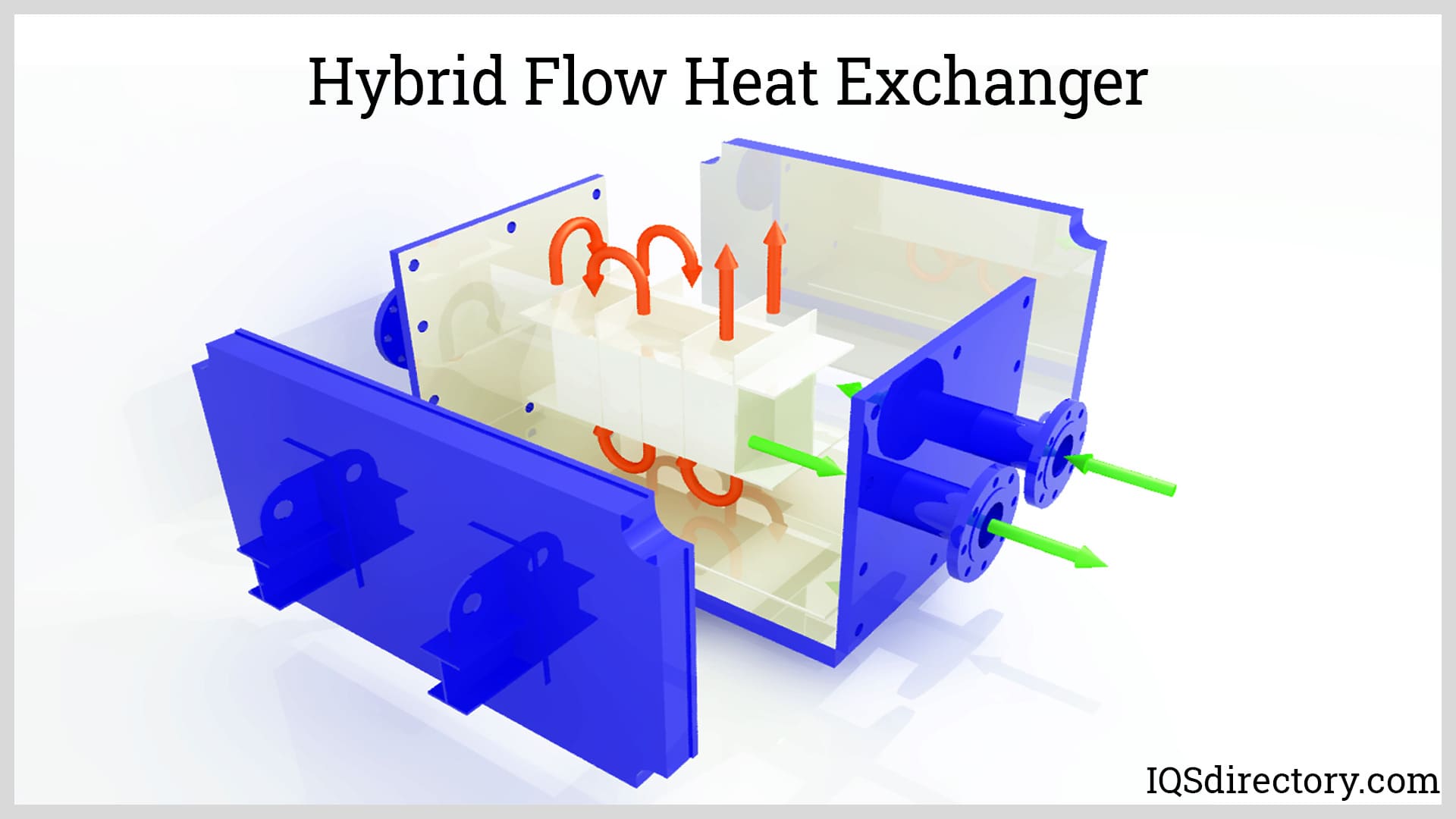

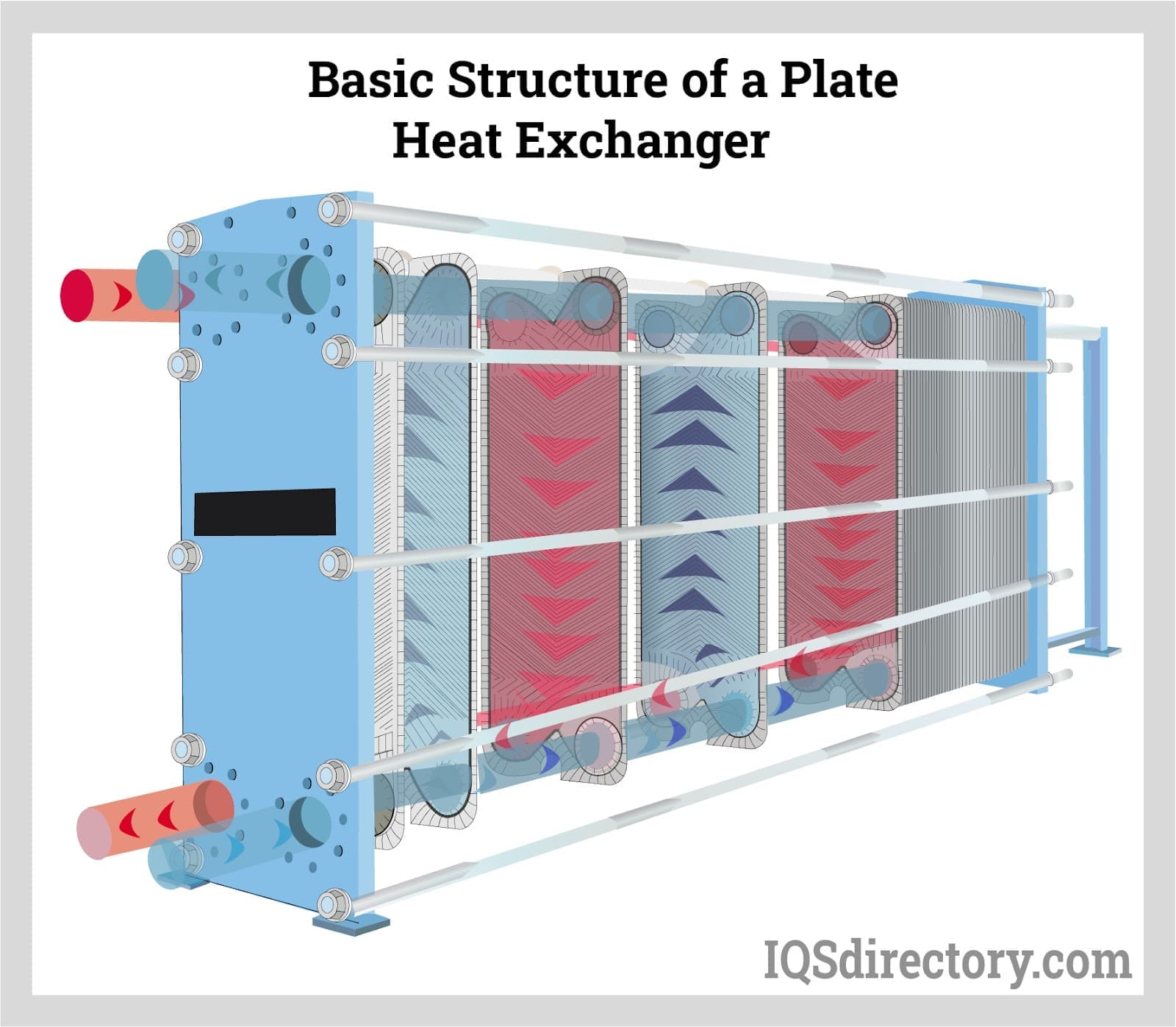
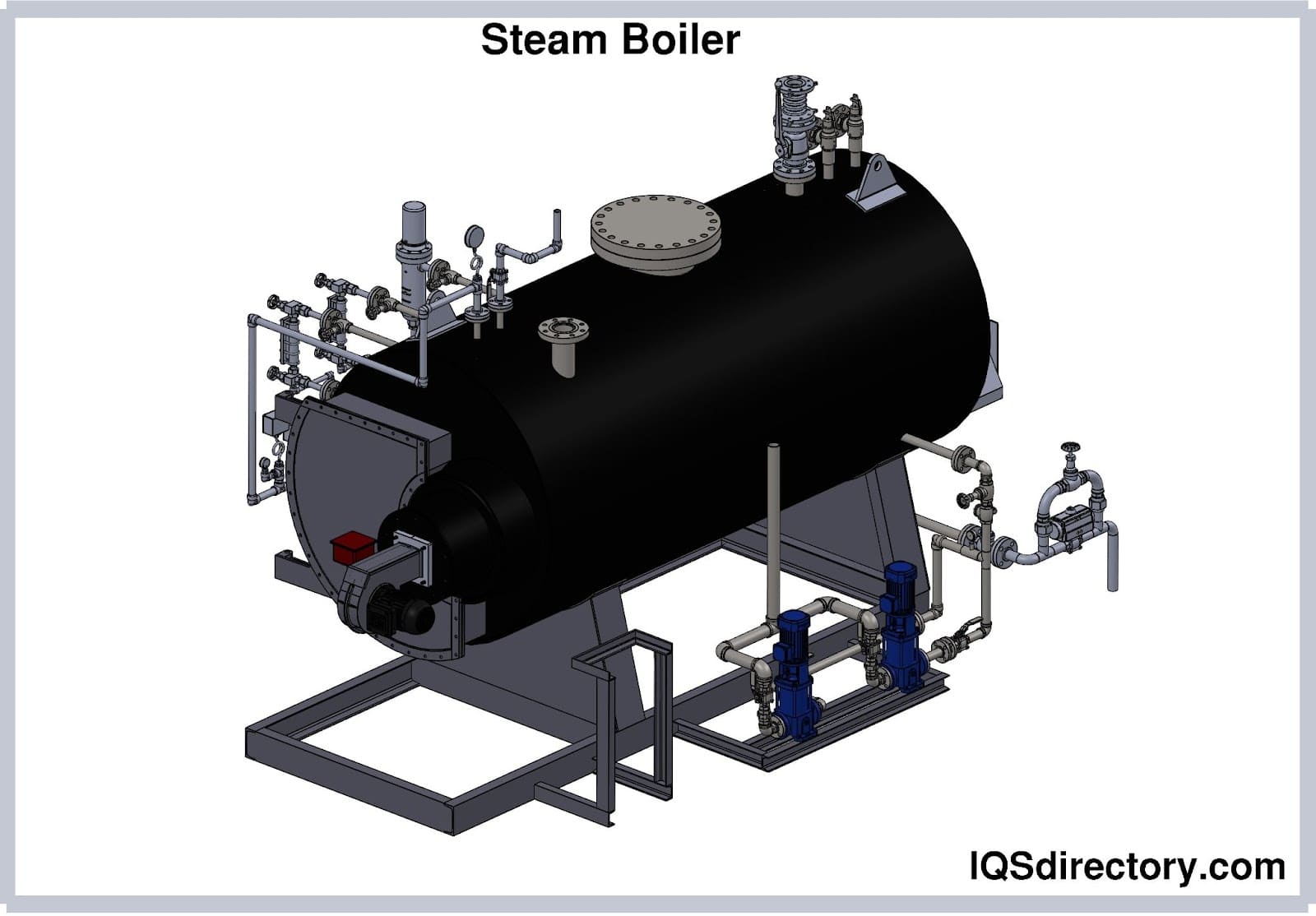
 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services