Air cooled chillers are a cooling system that uses a shell and tube evaporator to exchange heat. A refrigerant system removes heat from the water and transfers the heat to the air around the chiller. Air cooled chillers are very compact, easy to install, and exceptionally efficient. Read More…
Our customers know they can trust us for the ultimate in quality, affordability, and flexibility. If you want a fully customized solution for your chillers, we can help! We work hard to create the best solution for each of our customers, because we know that if you are not happy, we are not happy! You can learn more about our services by visiting our website or giving us a call today!

Dimplex Thermal Solutions, based in Kalamazoo, Mich., and home of Koolant Koolers, has been manufacturing water, air, and glycol chillers since 1952. Since that time Dimplex has expanded it’s product offering to include industrial cooling for: Machine Tooling, Food Processing and Packaging, Medical Diagnostic Imaging, Laser Cutting, Manufacturing Processes and more. Dimplex is known for their...
At Tark Thermal Solutions, we position ourselves as a dedicated partner in advanced cooling technology, delivering liquid chillers that support precise temperature control across demanding applications. We design and build our systems with a focus on reliability, thermal stability, and energy efficiency, tailoring each unit so it performs consistently in environments where process accuracy...
We are ChillX Chillers, and we take pride in engineering and manufacturing reliable, high-performance chillers designed to meet the cooling needs of businesses across a wide range of industries. Our focus has always been on combining innovation, energy efficiency, and durability, which is why our chillers are trusted for everything from process cooling and manufacturing applications to...
More Air Cooled Chiller Manufacturers

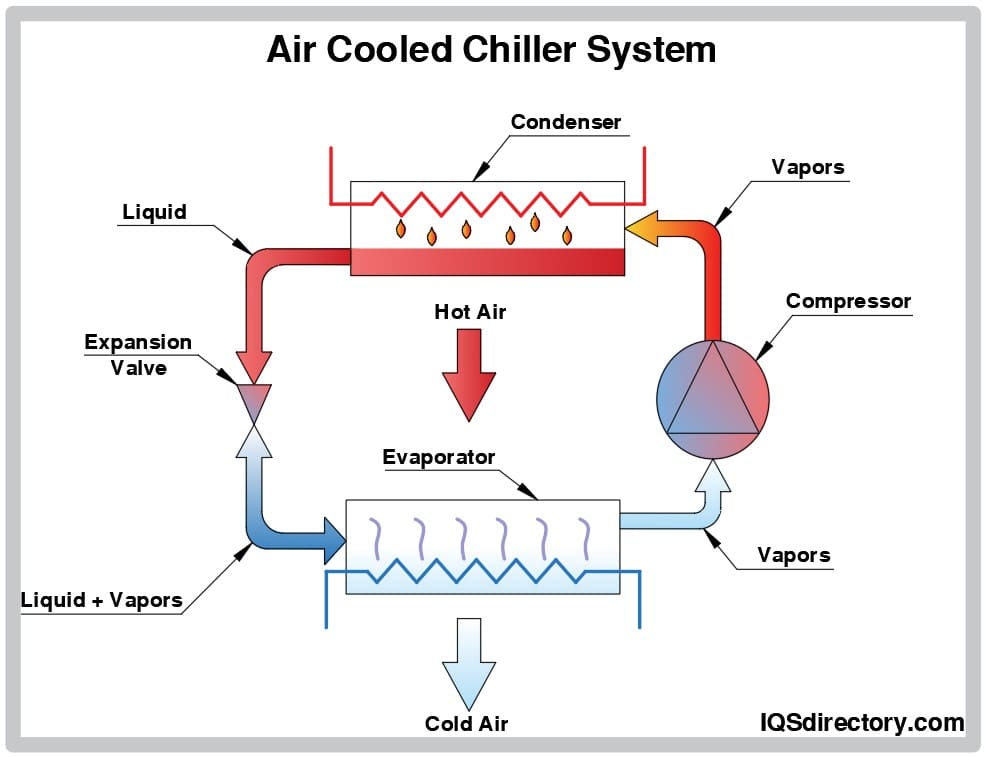
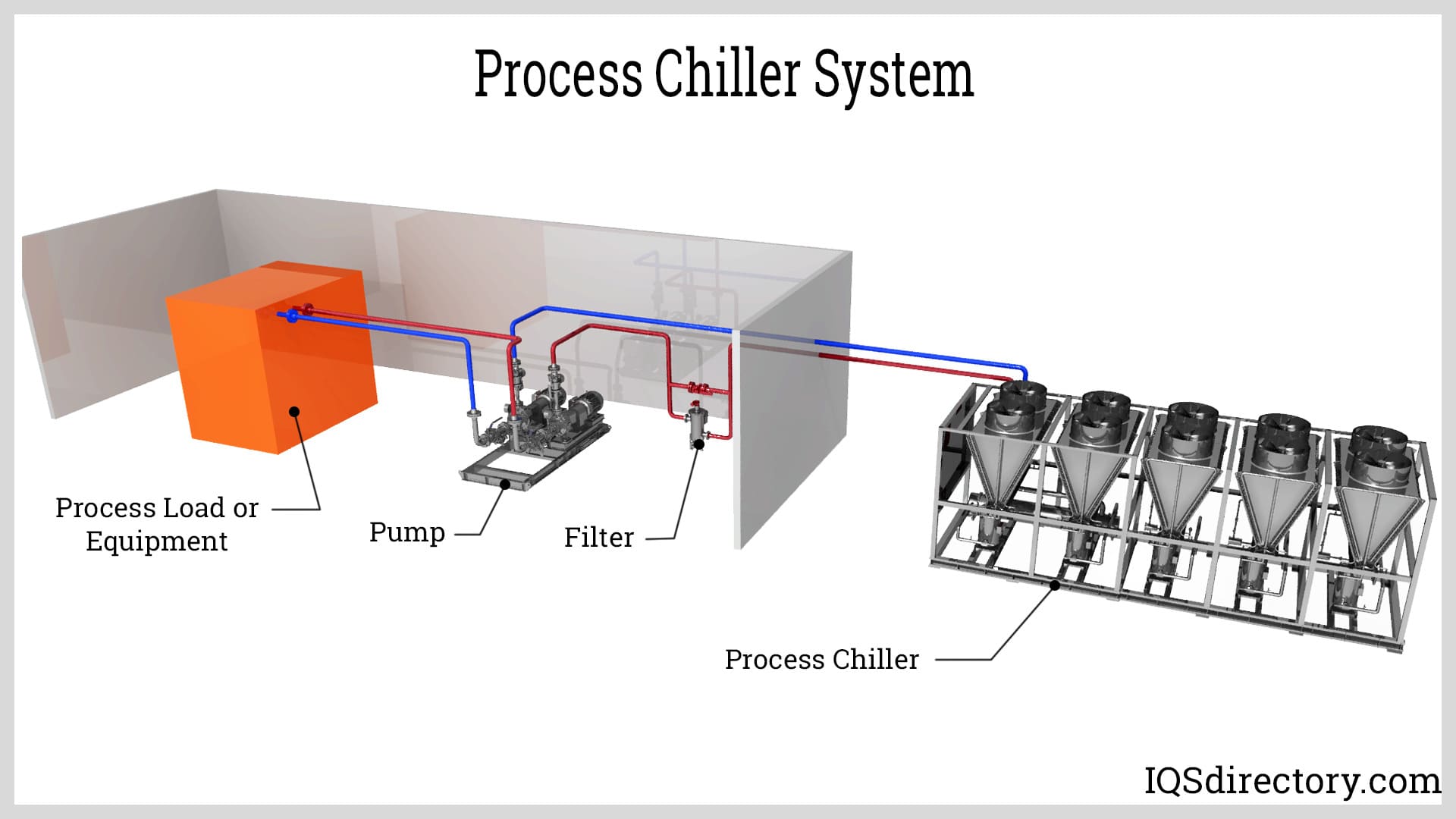
How Air Cooled Chillers Work
The size and design of air cooled chillers make them very popular for commercial and office buildings. Since they do not require a cooling tower, they can be portable and located on the top of a building or the ground near a building. Air cooled chillers remove heat from the water and harmlessly eject the hot air into the atmosphere and environment.
Components of an air cooled chiller:
-
Compressor
Compressors for air cooled chillers can be screw, scroll, or reciprocating.
-
Scroll Compressors
A scroll compressor has a scroll that orbits inside the housing. As the scroll orbits, it forces gas to the center of the scroll, where the gas reaches discharge pressure and is released.
-
Screw Compressor
Screw compressors are found in large cooling units with sizes of 20 to 300 tons and can be externally or internally driven. The helical rotors of a screw compressor trap and compress gasses.
-
Reciprocating Compressor
A reciprocating compressor is like an engine with a cylinder, piston, and a rod to achieve compression. An electric motor supplies the power for the unit. The piston is moved inside the cylinder by the rotation of a crank attached to the rod. When the piston moves backward, it pulls in the gas. As the piston moves forward, it compresses the gas before it is released.
-
-
Condenser
The four parts of a condenser are the housing, coils, compressor, and fan. Although there are a wide variety of designs for condensers, they all work following the same basic principle. The main part of the condenser is the coils, which are made of copper or aluminum and contain the refrigerant.
-
Fans
Fans pull air across the condenser's coils and force it out of the unit into the atmosphere.
-
Expansion Valve
The expansion valves control the flow of refrigerant and help change liquid refrigerant to gas for the evaporator. The evaporator core would freeze if there is too much refrigerant flow or be inefficient if the flow is too low.
-
Evaporator
In the evaporator, chilled water is produced, and the heat from warm water is removed and sent to the condenser.
Cooling Process of an Air Cooled Chiller
Step One
The compressor provides the force that drives the refrigerant, which leaves the compressor headed to the condenser at high pressure and temperature and as a superheated vapor.
Step Two
In the condenser, the refrigerant makes its way through coiled horizontal pipes transferring thermal energy into the air stream. The heated air is moved along by fans placed on the unit.
Step Three
The expansion valve holds the refrigerant to maintain its high pressure. The small orifice of the valve permits small amounts of refrigerant to continue to flow. However, as it enters the other side of the valve, the refrigerant experiences a pressure drop, turns into a vapor, and reaches a very low temperature.
Step Four
When the low-temperature refrigerant leaves the expansion valve and enters the evaporator, it passes through another set of horizontal tubes where it is surrounded by chilled water. The water and the refrigerant flow in opposite directions. During this process, the refrigerant picks up the unwanted heat from the water, which leaves with its thermal energy gone and at a very low temperature.
Types of Air Cooled Chillers
Air cooled chillers are used where the discharge of heat from the chiller is not a concern. In areas with cold temperatures, the discharged heat is used to heat buildings, manufacturing plants, and industrial operations. The primary types of air cooled chillers are stationary and portable. The compact design of air cooled chillers makes it possible to place them in various locations. Although they are compact and can be portable, they still provide a highly efficient cooling system.
Stationary Air Cooled Chillers
A stationary air cooled chiller is the central part of a cooling system and is normally never moved. Therefore, it has all the characteristics of an air cooled chiller with the same type of efficiency and stability. Stationary air cooled chillers are referred to as central cooling chillers and are used where the release of heat from the chiller is not an issue.
Portable Air Cooled Chillers
Portable air cooled chillers offer the convenience of being able to be moved to meet the needs of a location. They are used for various applications, from temporary cooling of a location to permanent cooling of factory operations.

Benefits of Air Cooled Chillers
The many benefits of air cooled chillers make them an ideal solution for various cooling applications.
- Air cooled chiller condenser coils always have plenty of fresh air. When the refrigerant reaches the condenser coils, the fresh air absorbs the heat.
- The proportional integral derivative (PID) temperature controller prevents harm from high temperatures and has a set scale that can be used to shut off the unit.
- Cooling fans connected with the condenser provide a constant fresh air supply.
- Heat is exchanged by the liquid refrigerant in a corrosion-resistant shell and tube heat exchanger.
- A key benefit of air cooled chillers is that they are environmentally friendly since they do not release toxic fumes or chemicals.
Selecting the Correct Air Cooled Chiller Supplier
For the most positive outcome when purchasing an air cooled chiller from an air cooled chiller supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our list of air cooled chiller companies. Each air cooled chiller company has a business profile page illustrating their areas of expertise and capabilities. A contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information, or to request a quote, is included. Review each air cooled chiller company website using our patented website previewer to get a better idea of what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple companies using the same form.







 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services