Laser chillers cool laser equipment and processes to help them perform at peak efficiency. Lasers are a form of cutting tool that produces a great deal of energy and heat. Although this is a necessary part of the process, excessive heat can damage equipment and produce poor-quality products. Read More…
Our customers know they can trust us for the ultimate in quality, affordability, and flexibility. If you want a fully customized solution for your chillers, we can help! We work hard to create the best solution for each of our customers, because we know that if you are not happy, we are not happy! You can learn more about our services by visiting our website or giving us a call today!

Dimplex Thermal Solutions, based in Kalamazoo, Mich., and home of Koolant Koolers, has been manufacturing water, air, and glycol chillers since 1952. Since that time Dimplex has expanded it’s product offering to include industrial cooling for: Machine Tooling, Food Processing and Packaging, Medical Diagnostic Imaging, Laser Cutting, Manufacturing Processes and more. Dimplex is known for their...
At Tark Thermal Solutions, we position ourselves as a dedicated partner in advanced cooling technology, delivering liquid chillers that support precise temperature control across demanding applications. We design and build our systems with a focus on reliability, thermal stability, and energy efficiency, tailoring each unit so it performs consistently in environments where process accuracy...
We are ChillX Chillers, and we take pride in engineering and manufacturing reliable, high-performance chillers designed to meet the cooling needs of businesses across a wide range of industries. Our focus has always been on combining innovation, energy efficiency, and durability, which is why our chillers are trusted for everything from process cooling and manufacturing applications to...
More Laser Chiller Manufacturers
Therefore, various types of chillers are used to control the generated heat, which assist in maintaining the power of the laser and its efficiency.

Heat generation is a common part of industrial manufacturing. In order to control the produced heat, various types of chillers have been developed that are designed to remove heat and cool applications. Lasers operate at temperatures that are extremely high to be able to make precision and highly accurate cuts. Chillers regulate temperature so lasers do not overheat and prevent damage to components and parts.
Benefits of Chillers for Lasers
The rapid advancement of lasers has made them an ideal and necessary tool for manufacturing. The key component for the laser process is heat, which has to be generated sufficiently to melt the surface of the material being cut. As important as the heat is to the process, it is just as important to have it removed. The best way to complete the removal is by using reliable industrial chillers.

-
Sustains Power
As the temperature increases in a laser, its wavelength increases, causing the beam to fluctuate and diminish its performance. With the increase in heat, the head of the laser begins to vibrate and lose accuracy. This condition must be controlled to avoid inaccuracies and poor-quality products. Industrial chillers are used to ensure uniform outputs and precision dimensional accuracy.
-
Stress
Laser systems are under constant stress with frequent temperature changes. They are designed to withstand heavy workloads but must be cooled to perform optimally. In those conditions, cool air chillers blow ambient air onto heat exchangers to remove hot air and lessen the potentiality of defective production.
-
Lifespan
All industrial equipment has to endure the demands of production and manufacturing. Keeping the equipment in top condition is necessary for profitability and meeting production deadlines. Laser industrial chillers provide a tool that alleviates the potential harm caused by overheating, including damage to lasers and a significant decrease in efficiency.

-
Flow Rate
Laser cutting produces a great deal of heat that has to be controlled and managed at a steady and stable temperature. A laser chiller guarantees the proper conditions and the ability to maintain a constant and consistent flow rate.
What is a Laser Chiller?
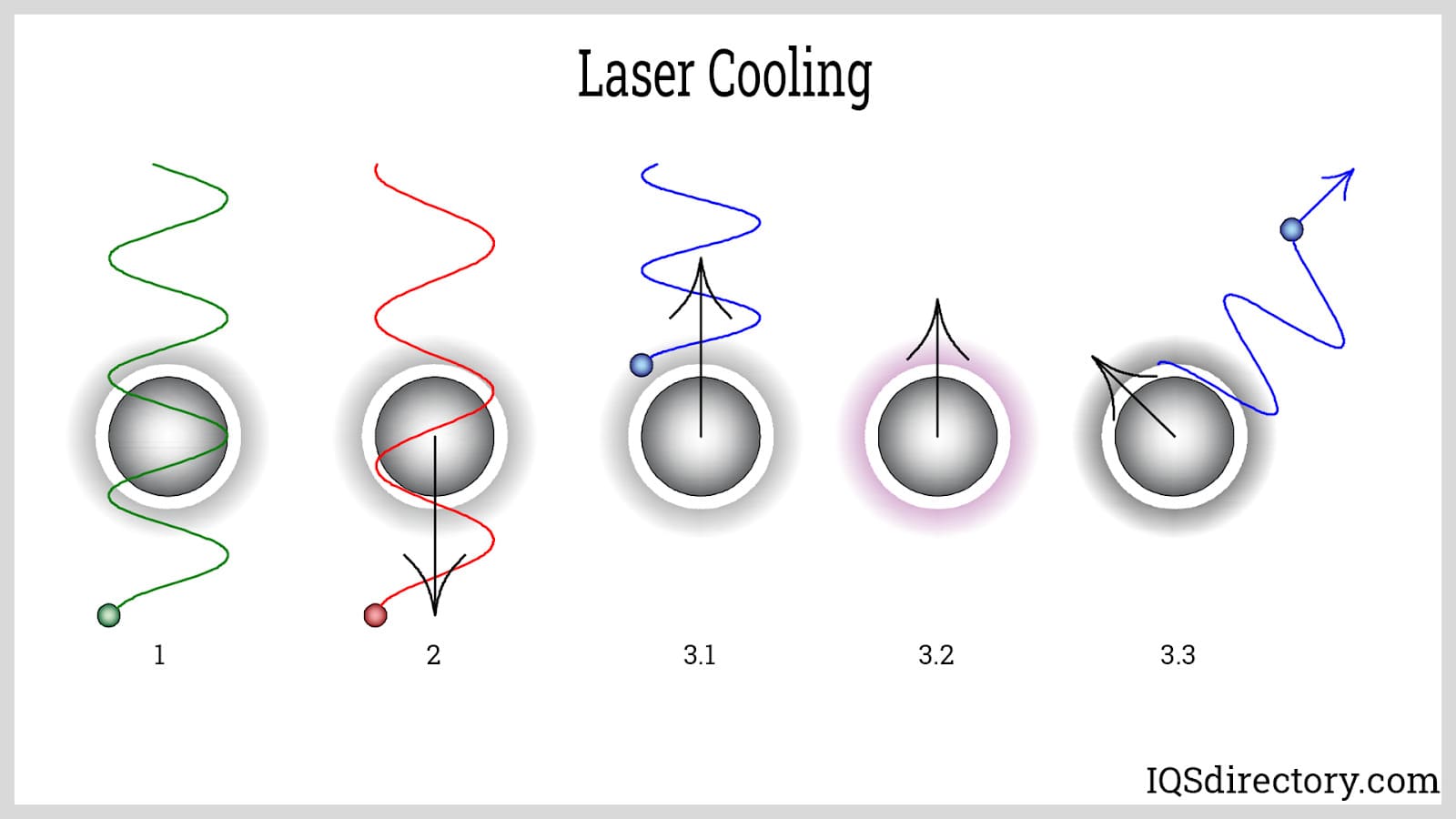
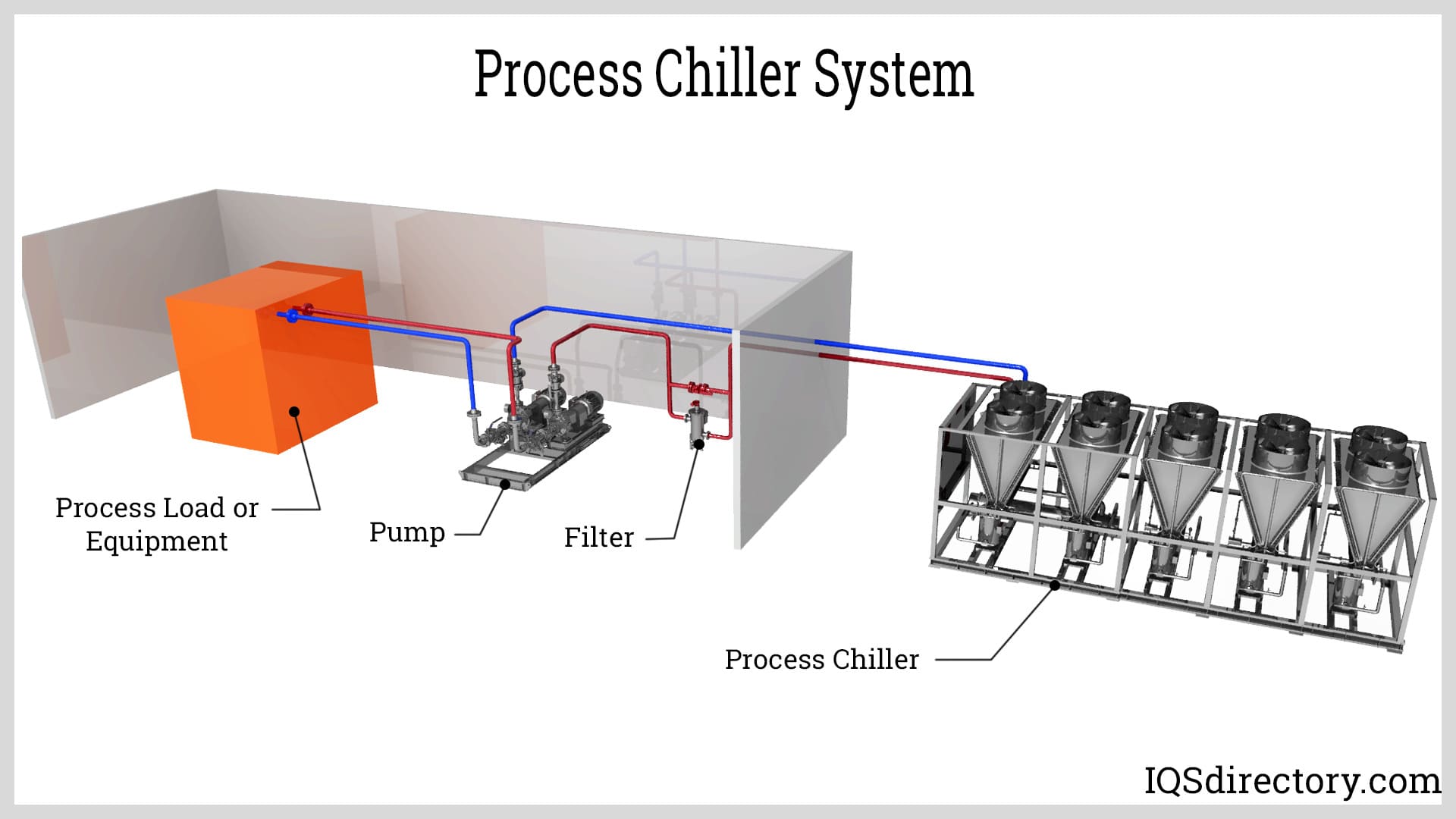
A laser chiller uses vapor compression to remove laser machine heat. Chilled water circulates through laser tubes and absorbs the waste heat released in the condenser. A central component for any chiller is the compressor that compresses the refrigerant gas to increase its pressure to remove heat in the condenser, which can be air cooled or water cooled.
The term chiller normally refers to a large device capable of cooling a building, factory, or manufacturing facility. Laser chillers are a special type of compact chiller with small compressors, condensers, evaporators, expansion valves, and drive boards. A recirculating pump, fluid reservoir, and fittings connect the chiller to the laser's cold plate.
Laser Chiller Components
-
Evaporator
Low-pressure refrigerant enters the evaporator where heat from the laser boils the refrigerant and changes it from a low-pressure liquid to a low-pressure gas.
-
Compressor
The low-pressure gas enters the compressor, which can be a screw, reciprocating, or centrifugal type. In the compressor, the low-pressure gas is compressed into a high-pressure gas to enter the condenser.
-
Condenser
In the condenser, the high-pressure gas has its heat removed, which turns it into a high-pressure liquid.
-
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve controls the amount of refrigerant that can enter the evaporator, where the cooling cycle begins again.

Cooling High Powered Lasers
High-powered lasers depend on cooling due to the heat they generate, which must be removed from the laser system. Carbon dioxide lasers, excimer lasers, solid-state lasers, and die lasers are liquid-cooled. This process helps maintain precision laser wavelengths and high output efficiency, achieves beam quality, and reduces thermal stress.
Large gas and high-powered lasers must have external water flowing through the light-generating section of the laser system. Ion lasers can produce 5kW up to 55 kW heat waste as a by-product of a laser system. Such heat levels necessitate the use of a laser chiller. In all cases, with that amount of heat, a high-powered laser system will be more efficient with less heat.
Removing heat from a high-powered laser system is necessary since an increase in temperature results in an increase in wavelength that can compromise laser performance. The diode laser wavelength increases with temperature, necessitating a uniform temperature throughout the diode array for high optical conversion efficiency. Laser chillers for high-powered lasers rely on recirculating chillers to achieve the necessary requirements.
Compressor-based recirculating chillers reach temperatures of 23 °F to 95 °F (-5 °C to 35 °C) with stability of ±0.1°C. In addition, recirculating chillers are environmentally friendly and cost-effective since they rely on tap water for their processing. They are used where there is high heat flux, high ambient temperatures, and when a laser system necessitates a chilled environment, such as with an excimer laser.
Cooling Low Power Lasers
Low power lasers, such as helium neon or argon ion lasers, may not require heat removal or come with cooling fans. Some versions have a built-in cooling system, such as a closed loop heat exchanger. Low power lasers use passive cooling through heat sinks or convection. Cooling can be assisted by a thermoelectric cooler that pumps heat from the laser to a heatsink or radiator.
In all cases, low power lasers do not produce sufficient heat that would require using a laser chiller, regardless of its size. Unlike high-powered lasers, low-powered lasers have a weak beam and are designed for less aggressive production tasks.
Choosing the Right Laser Chiller Manufacturer
For the most beneficial outcome when purchasing a laser chiller from a laser chiller manufacturer, it is critical to compare several companies using our directory of laser chiller companies. Each laser chiller manufacturer has a business profile page highlighting their areas of expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly contact the manufacturer for more information or to request a quote. Review each laser chiller business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple businesses with the same form.







 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services