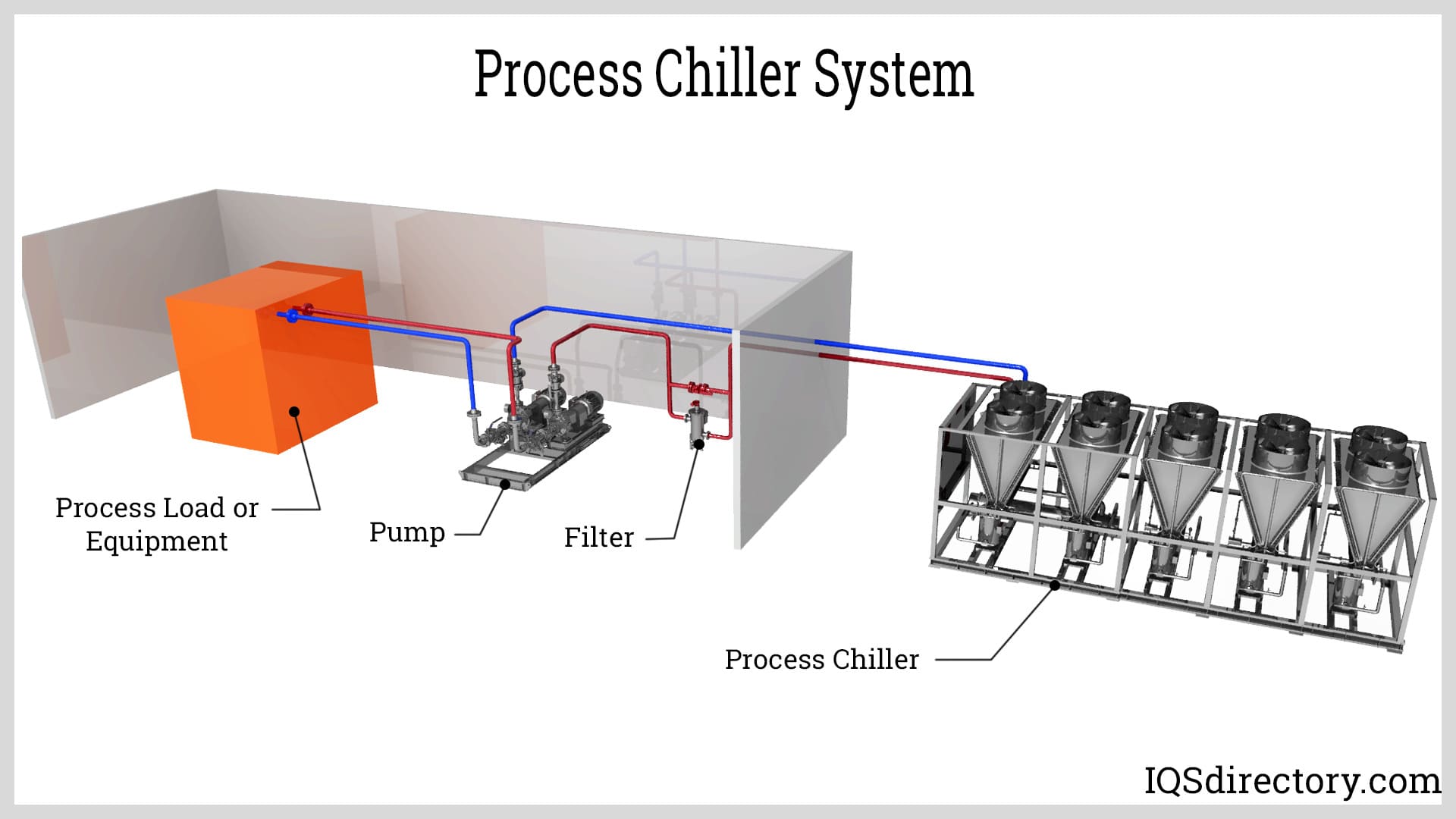
Process chillers are used for products that require specific cooling temperatures to ensure the quality of the product. They are commonly used in breweries, dairies, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industrial processes that require temperature control. Process chillers have the same structure and design as all chillers: a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve. Read More…
Our customers know they can trust us for the ultimate in quality, affordability, and flexibility. If you want a fully customized solution for your chillers, we can help! We work hard to create the best solution for each of our customers, because we know that if you are not happy, we are not happy! You can learn more about our services by visiting our website or giving us a call today!

Dimplex Thermal Solutions, based in Kalamazoo, Mich., and home of Koolant Koolers, has been manufacturing water, air, and glycol chillers since 1952. Since that time Dimplex has expanded it’s product offering to include industrial cooling for: Machine Tooling, Food Processing and Packaging, Medical Diagnostic Imaging, Laser Cutting, Manufacturing Processes and more. Dimplex is known for their...
At Tark Thermal Solutions, we position ourselves as a dedicated partner in advanced cooling technology, delivering liquid chillers that support precise temperature control across demanding applications. We design and build our systems with a focus on reliability, thermal stability, and energy efficiency, tailoring each unit so it performs consistently in environments where process accuracy...
We are ChillX Chillers, and we take pride in engineering and manufacturing reliable, high-performance chillers designed to meet the cooling needs of businesses across a wide range of industries. Our focus has always been on combining innovation, energy efficiency, and durability, which is why our chillers are trusted for everything from process cooling and manufacturing applications to...
More Process Chiller Manufacturers
However, they vary from other chillers because they cool as a part of production and manufacturing processes.

Process chillers can be air cooled or water cooled, with water cooled process chillers having a cooling tower. A unique feature of process chillers is their ability to withstand the harsh conditions of manufacturing environments. Their durable design is necessary for them to adapt to the requirements of an industrial processing application.
Process Chiller Phases
All chillers have four basic components (an evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve) that work together to complete the cooling process. Each component performs a vital role in ensuring that the proper process temperature is achieved. The various components undergo a thermodynamic process during cooling in four phases.
Phase One
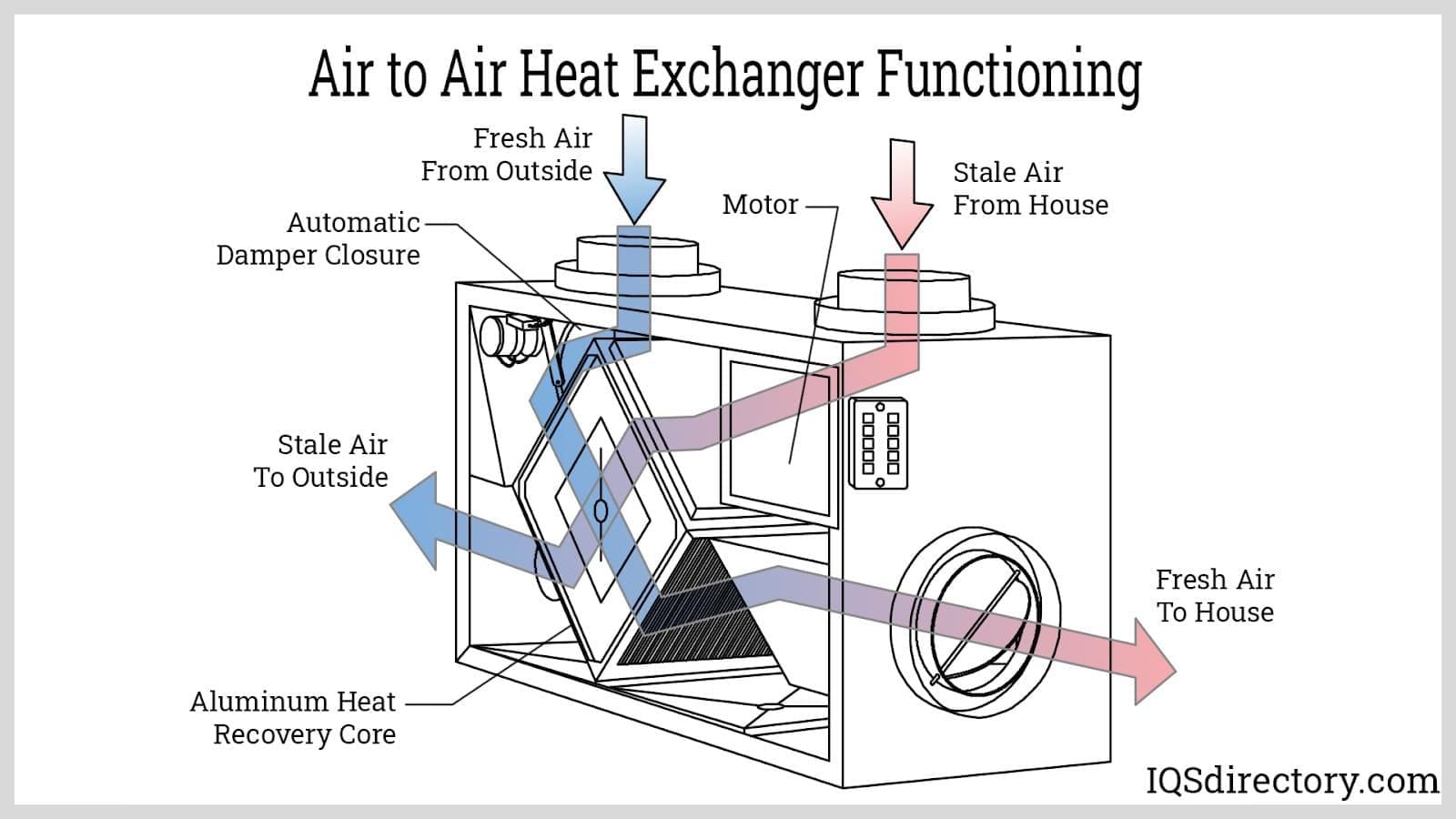
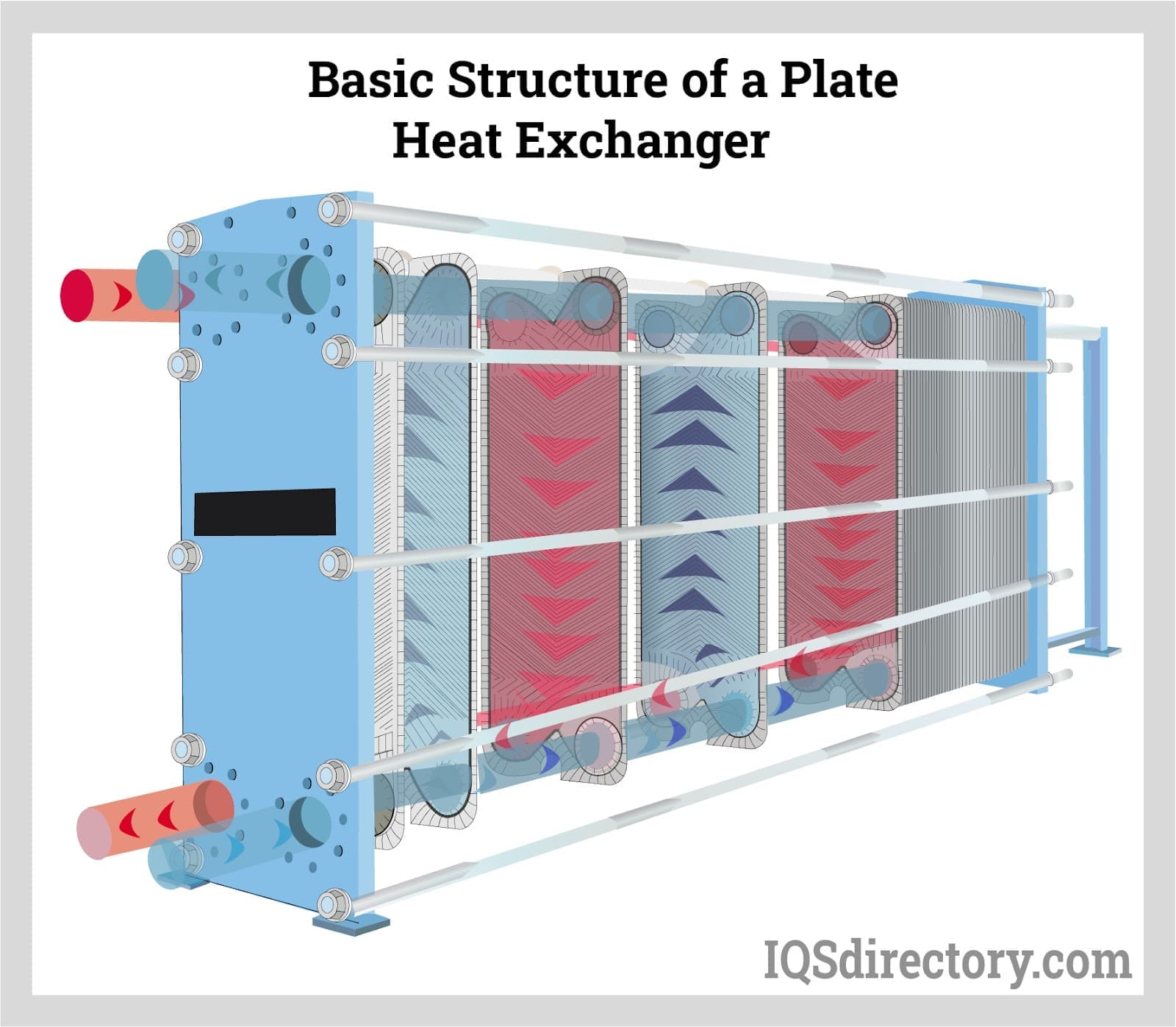
The evaporator acts as a heat exchanger that collects and places heat in the refrigerant. The collected process heat boils the refrigerant, which changes it from a liquid to a low-pressure gas. During this phase, the coolant temperature lowers. Three types of evaporators are shell and tube, coil, and plate.
-
Shell and Tube
Shell and tube evaporators are highly efficient and compact. The refrigerant passes from the expansion valve into the tubes, where the refrigerant evaporates.
-
Coil
The refrigerant enters the coils from the expansion valve, where it is cooled in the coils before moving to the compressor.
-
Plate
Plate evaporators have plates over which a thin liquid film passes to initiate evaporation.
Phase Two
From the evaporator, the low-pressure gas moves to the compressor at a low temperature, where it will be compressed to raise its temperature and pressure. Pressure and temperature increase are necessary for the heat from the refrigerant to be released in the condenser. The varieties of compressors include screw, scroll, centrifugal, and reciprocating. Each type compresses the refrigerant gas using different mechanisms.

Phase Three
Phase three is when the refrigerant enters the condenser under high pressure and at a high temperature. In the condenser, the heat is removed from the refrigerant, which changes from a gas to a liquid. Air or water is the cooling source in the condenser; fans are used for air cooling while water is used for water cooling.

Phase Four
At this phase, the heat from the process has been released, and the refrigerant is ready for reprocessing. A process chiller's structure moves the refrigerant from the evaporator to the condenser so that the heat from the manufacturing process is constantly removed. Between the condenser and the evaporator is the expansion valve, structured to control the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
Process Chiller Applications
There are endless uses for process chillers due to their flexibility and the need for cooling for many processes. For a product to meet its designed requirements, it must be produced at a specific temperature so that the method of production does not alter its properties. Process chillers cool both products and machinery during production.
Food Processing
Refrigeration is a vital part of the preservation and stability of foods and is the most common application for which cooling is required. Additionally, chillers are used in food production to ensure that products are kept at a constant temperature, especially in producing alcoholic beverages that temperature fluctuations can severely damage.

Metal Plating
The process of metal plating involves high-temperature electroplating or electroless plating. High temperatures are necessary to ensure a tight bond of the finish to the metal. Each process requires temperatures well over 300 °F (148.9 °C), which requires heavy-duty process chillers to remove the heat. The exceptionally elevated temperatures and harsh conditions demand the use of process chillers that are resilient enough to withstand the conditions.
Plastic Production
Plastic production is a process that requires the most precise and accurately controlled temperatures to avoid producing damaged or inferior products. The process has little margin for error since intense and elevated heat can melt the plastic and destroy a production run. Although the molds for plastic production do not have to achieve exceptionally high temperatures, their continual use requires that they remain heated for several hours.
In the case of extruded plastics, the extruded plastic has to be cooled in a bath at exactly the correct temperature. The bath water must also be circulated and cooled at each run. For cast plastic and extruded plastic, process chillers provide the necessary temperature control to ensure the quality of the products produced.

Critical Aspects of a Process Chiller
Certain characteristics and traits must be investigated when deciding to purchase a process chiller, the key factor of which is longevity and reliability. The quality of a product may depend on the performance of a process chiller, so as with all industrial equipment, its selection should be carefully considered.
Other critical aspects include:
- Strength of Performance
- Temperature Control
- Hours of Continuous Operation
- Capacity
- Customization
- Control Mechanism
- Environmental Factors – Energy Efficiency
- Reliability and Dependability
- Process and Application
- Footprint
Choosing the Correct Process Chiller Company
For the most beneficial outcome when purchasing a process chiller from a process chiller company, it is important to compare several manufacturers using our list of process chiller companies. Each company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of expertise and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with them for more information or request a quote. Review each process chiller company website using our patented website previewer for a better idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple businesses with the same form.







 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services