Recirculating chillers create high-pressure flow using a coolant fluid or refrigerant to lower temperatures to meet application specifications. They have a closed loop system that uses the same fluid to complete the cooling process. Recirculating chillers use air or water for heat dissipation and are a cost-effective and efficient cooling process. Read More…
Our customers know they can trust us for the ultimate in quality, affordability, and flexibility. If you want a fully customized solution for your chillers, we can help! We work hard to create the best solution for each of our customers, because we know that if you are not happy, we are not happy! You can learn more about our services by visiting our website or giving us a call today!

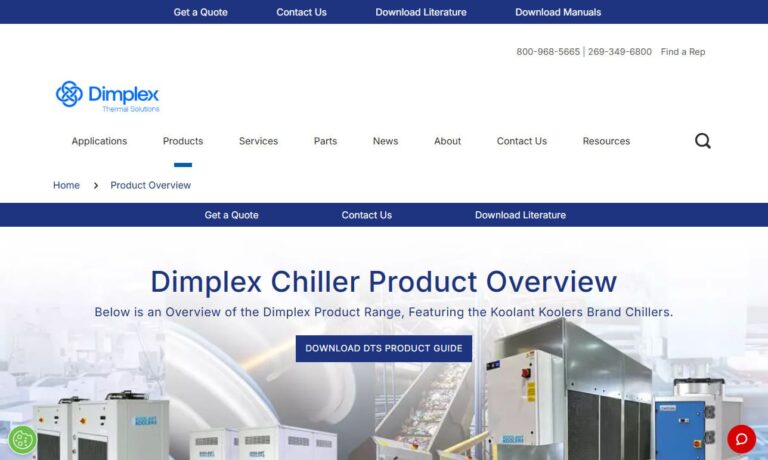
Dimplex Thermal Solutions, based in Kalamazoo, Mich., and home of Koolant Koolers, has been manufacturing water, air, and glycol chillers since 1952. Since that time Dimplex has expanded it’s product offering to include industrial cooling for: Machine Tooling, Food Processing and Packaging, Medical Diagnostic Imaging, Laser Cutting, Manufacturing Processes and more. Dimplex is known for their...
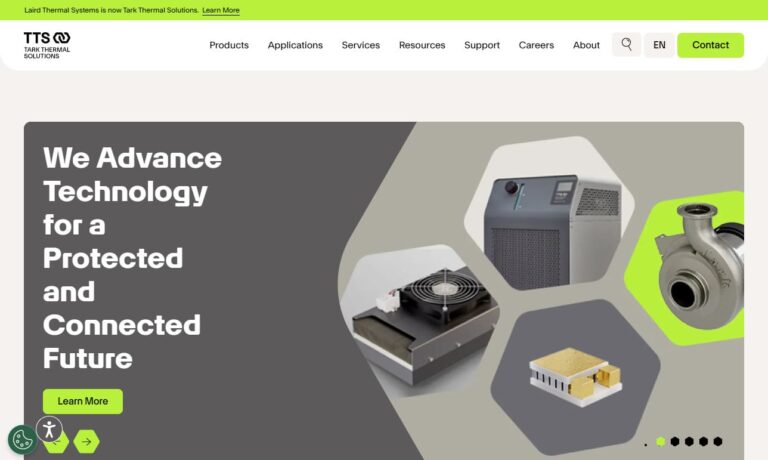
At Tark Thermal Solutions, we position ourselves as a dedicated partner in advanced cooling technology, delivering liquid chillers that support precise temperature control across demanding applications. We design and build our systems with a focus on reliability, thermal stability, and energy efficiency, tailoring each unit so it performs consistently in environments where process accuracy...
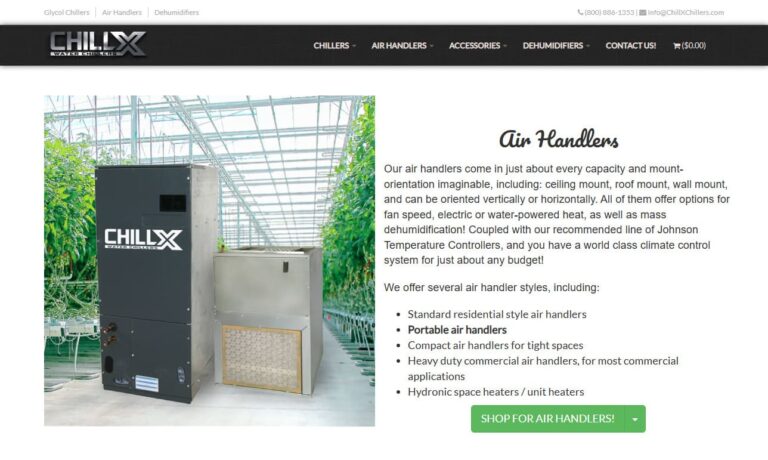
We are ChillX Chillers, and we take pride in engineering and manufacturing reliable, high-performance chillers designed to meet the cooling needs of businesses across a wide range of industries. Our focus has always been on combining innovation, energy efficiency, and durability, which is why our chillers are trusted for everything from process cooling and manufacturing applications to...
More Recirculating Chiller Manufacturers

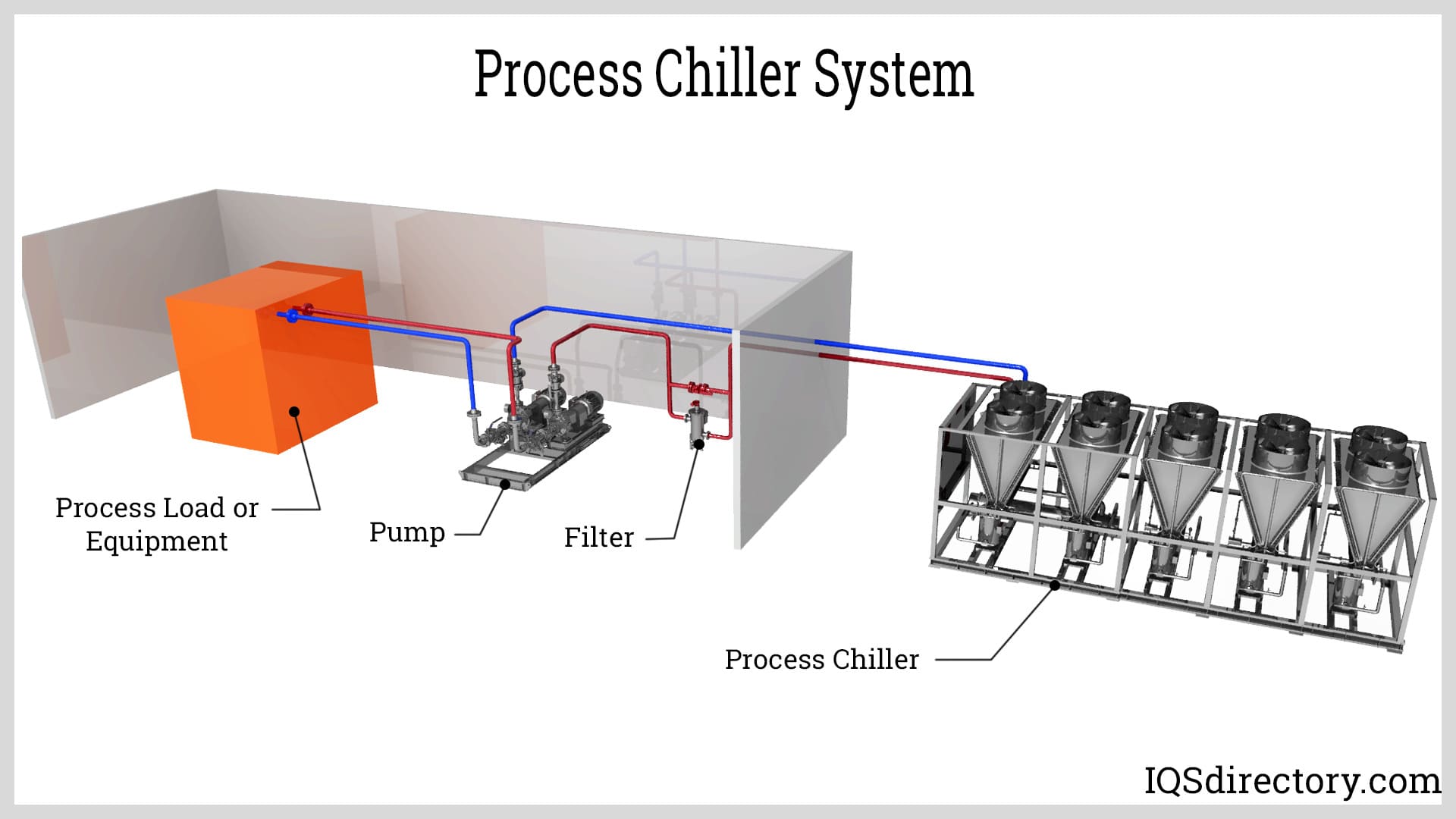
A key characteristic of recirculating chillers is their ability to provide precise and continuous temperature control through the recirculation of the coolant. They are compact, self-contained cooling units that are exceptionally resilient and reliable. The purpose of recirculating chillers is to eliminate mechanical and electrical heat by pulling air from a process or space and removing or releasing the heat in the air. Modern manufacturing processes require precise thermal control to ensure the success of a process. Recirculating chillers provide the instrumentation and control necessary to achieve successful and positive results.
Recirculating Chiller Process
A recirculating chiller uses coolant circulation and high-pressure flow to enhance and speed up the heat removal and cooling processes. They have the same components as all types of chillers: a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator.

Evaporator
The cooling process for a recirculating chiller begins with the refrigerant entering the evaporator, where it is transformed from a liquid to gas using the heat extracted from the cooling process. The gas created by the evaporator has a very low pressure that must be changed to enter the condenser. Several different designs of evaporators are used by recirculating chillers and include coil evaporators, which are the most commonly used.

Compressor
Compressors for recirculating chillers are normally scroll or screw, which are capable of fitting a recirculating chiller's design. The purpose of the compressor is to take the low-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant from the evaporator and raise them to meet the requirements of the condenser.
- Scroll Compressors – Scroll compressors have two spiral disks placed over one another. One of the disks is static, while the other rotates around the static disk. During the disk's rotation, the refrigerant gets caught in pockets of air, where its pressure and temperature increase.
- Screw Compressors – Screw compressors have rotating helical screws, male and female, that mesh together to compress the refrigerant gas before sending it on to the condenser.
Condenser
The condenser is where the heat from the process of the compressor is dissipated. In the condenser, heat is released from the refrigerant and removed by water or air circulation. In most recirculating chillers, the removal process is completed by a fan or blower. Removal of the heat decreases the temperature of the refrigerant, which causes it to return to liquid form. The recirculation process begins when the liquified refrigerant leaves the condenser. The refrigerant remains in the system to be returned to the process through the expansion valve between the condenser and evaporator.
Expansion Valve
As with other parts of a recirculating chiller, there are several types of expansion valves, all designed to control the flow, pressure, and temperature of the refrigerant. The expansion valve slowly releases the refrigerant at low pressure and temperature into the evaporator to restart the cooling process. Normally, recirculating chillers have thermostatic expansion valves that can be regulated by adjusting the temperature at which it will release the refrigerant. They are highly reliable and react quickly to adjustments.

Benefits of Recirculating Chillers
Recirculating chillers are highly efficient, easy to install, and exceptionally accurate cooling devices. They are widely used in many applications due to their economical operation and reliable performance. In addition, their ability to rapidly remove heat from an operation, process, or environment has made them one of the more popular types of chilling units.
- Reduced Waste – Methods that have been used for years to cool processes have been water, ice, and nitrogen oxide. Although they were effective, they required a great deal of wasted water that could not be reused. Recirculating chillers have eliminated the old cooling methods and replaced them with a process far exceeding the demands of any cooling needs.
- Efficiency – Of all of the characteristics of industrial devices, efficiency is the hallmark of a device's performance. The closed loop design of recirculating chillers makes them one of the most efficient types of chillers. Their ability to quickly produce the necessary temperatures reliably makes them an ideal cooling tool. Once a recirculating chiller is charged and operating, it provides constant and consistent cooling without fluctuation or variance.
- Cost – Along with the need for efficiency is the need for cost savings, which has become a major concern in today's business environment. Although the initial cost of a recirculating chiller may be high, it can be recouped through a recirculating chiller's longevity. Once a recirculating chiller is in operation, it requires little maintenance, offers exceptional performance, and seldom needs fluids, components, or parts replaced.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Recirculating Chiller
- Necessary Temperature Range – Recirculating chillers can reach a set point of -130 °F (-90 °C) and act as a heater maintaining a temperature of 302 °F (150 °C).
- Cooling Capacity – The chiller should match the cooling capacity needed for the application.
- Chiller Size – For a recirculating chiller to provide optimum performance, its capacity should match the application for which it is being used.
- Energy Use – For proper use, a recirculating chiller should have a flow rate that ensures that it provides accurate temperatures without using excess energy.
Choosing the Right Recirculating Chiller Business
To guarantee the most positive result when purchasing a recirculating chiller from a recirculating chiller manufacturer, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of recirculating chiller companies. Each recirculating chiller manufacturer has a business profile page highlighting their their areas of experience and capabilities, and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote, Review each recirculating chiller company website using our patented website previewer for an understanding of what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple companies with the same form.







 Boilers
Boilers Chillers
Chillers Cooling Towers
Cooling Towers Furnaces
Furnaces Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers Heat Transfer Equipment
Heat Transfer Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services